We ran user tests of fdroidserver, the tools for developers to create and manage F-Droid repositories of apps and media. This test was set up to gather usability feedback about the tools themselves and the related documentation. These tests were put together and run by Seamus Tuohy/Prudent Innovation.
Methodology
Participants completed a pretest demographic/background information questionnaire. The facilitator then explained that the amount of time taken to complete the test task will be measured and that exploratory behavior within the app should take place after the tasks are completed.
The participant was then provided a laptop with a browser window open to the F-Droid documentation. The facilitator let the participant know that if they felt they need anything external that they could ask the facilitator for that.
At the start of each task, the participant was provided the task, and shown the resources that were available for them to use on a USB stick provided by the facilitator. The participant was then instructed to read the task description from the printed copy and begin the task. Time-on-task measurement began when the participant started the task.
The facilitator instructed the participant to ‘think aloud’ so that they could capture their otherwise internal thoughts about interactions with the F-Droid server software. The facilitator observed and entered participant behavior, participant comments, and system actions into their record of the event.
After each task, the participant spoke with the facilitator about the task. After all task scenarios were attempted, the participant completed a post-test satisfaction questionnaire.
Task Completion
Each participant was asked to complete six specific tasks. At the start of each task, the participant was read the task, and shown the resources that are available for them to use. The participant was then instructed to read the task description from the printed copy and begin the task.
Tasks
- Set Up an F-Droid application repository with the applications on this USB Drive.
- Connect to that repository using the F-Droid client.
- Group the applications under your repositories name in the F-Droid interface.
- Download the barcode scanner application using the F-Droid client.
- Update your F-Droid repository with an update to the barcode scanner app.
- Download the update using the phone.
Tasks are marked as “complete” after the participant says they have completed the task or after the test facilitator has enough evidence that the task has been completed. Tasks are marked as “uncompleted” after the participant says they cannot complete the task and requests assistance.
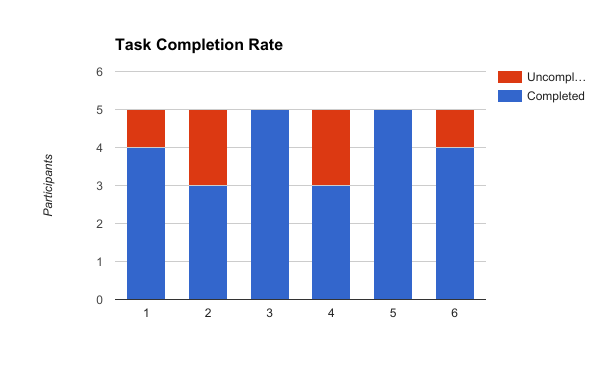
Task Completion Time
Test time will begin after the participant says they have understood the task and will begin. Testing time will end after the participant says they have completed the task or after the test facilitator has enough evidence that the task has been completed. In the case of a critical error, test time will stop after the participant says they cannot complete the task and request assistance.
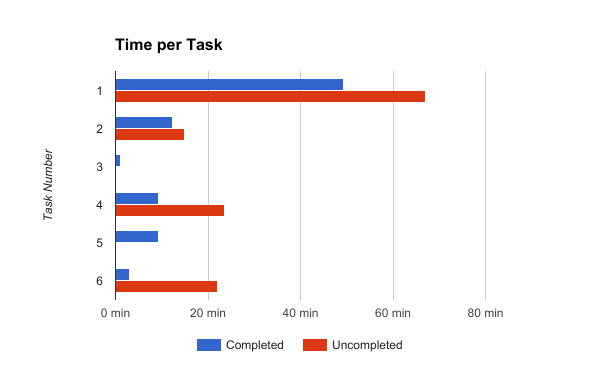
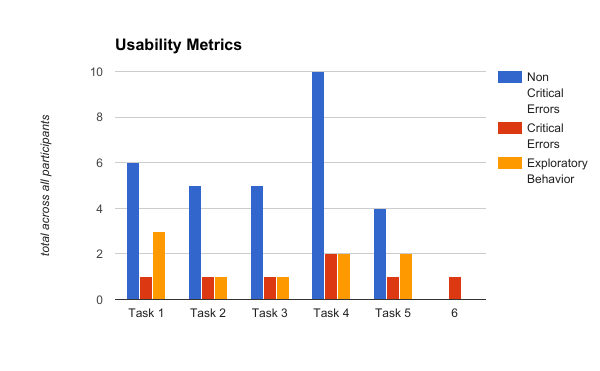
Usability Metrics
Usability metrics refers to participant performance when completing the assigned tasks. This is includes completion success rates, error rates, time to task completion and subjective evaluations/interviews.
- Critical Errors: Critical errors are reported as errors that result in failure to complete the task. Participants may or may not be aware that the task goal is incorrect or incomplete. Independent completion of the task is the goal; help from the test facilitator or others is to be marked as a critical error.
- Non-critical Errors: Non-critical errors are errors that the participant recovers from alone and are not such that the participant can no longer complete the task. They can include errors such as excessive steps taken to complete a task or initially using an incorrect function but recovering from that incorrect step.
- Exploratory Behavior: Errors that are off task from the main task attempting to be completed will be marked as exploratory behavior.
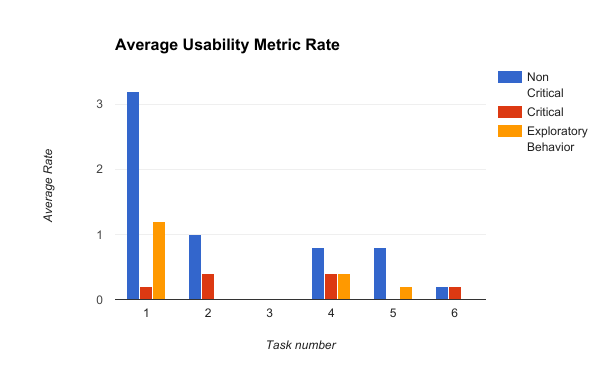
It should be noted that many of the errors that were encountered in tasks two, four, and six were the result of configuration decisions and non-critical errors in tasks one and five. More information about why this is the case can be found in the “Task Specific Findings.”
Task Specific Findings
Task 1: Set Up an F-Droid application repository with the applications on this USB Drive.
- Average Time: 53 Minutes
- Number of Participants with Critical Errors: 1
Docs needed for configuring the remote server
The participants were provided a remote server that was pre-configured to host F-Droid applications. The research team did this because setting up a web-server to host an F-Droid repository seemed out of scope, and it would increase the length of the UX session to an unacceptable length.
During this activity the participants were consistently confused by the documentation related to setting up the F-Droid host server (even though the server was pre-configured for them.) Documentation around file permissions on the remote server were especially troublesome.FOOTNOTE: Footnote
Feedback:
- The participant was confused about where the documentation begins to start deploying the server.
- The participant stated that there is not enough information on how to configure the remote server.
- It is missing in the documentation that before doing “fdroid server update” the permissions of the files to be served can be changed locally since they are transmitted to the remote server with the same local permissions.
- In the documentation, the information about the file permissions and configuration of the server at Fdroid level is missing. The documentation should say what permissions contain the generated files, (or what permissions they should contain).
- It is missing in the documentation that before doing “fdroid server update” the permissions of the files to be served can be changed locally since they are transmitted to the remote server with the same local permissions.
- The participant did not use the command fdroid server update to push the apps to the remote server, instead of that, he used the command SCP to send the data of manually.
- The participant was confused about the location of the files hosted on the web server. Doubt resolved after reviewing the documentation.
Confusing ordering of documentation
The participants felt that the documentation was confusingly ordered. While a few noted that the individual pieces of documentation were correct, and even clear once a participant is familiar with themFOOTNOTE: Footnote, the overall organization and ordering of documentation made it made it difficult to use.
Feedback:
- There were many doubts regarding the order of the steps, there was also a sensation of ordered list of steps when in practice the information were related to different activities (eg. Local Demo and Real World setup)
- The documentation is not understandable, not in terms of language but in the way of explaining, it should be more detailed. It feels difficult to understand for entry level people.
- The way information is presented and how it is structured seems to be disconcerting and overloaded.
- In outlines, poorly structured, getting started should have the section “set repo” and “install”, should not make emphasis on FAQs.
- The participant considers that documentation is confusing as to the step by step, he ends up diverting from the task received.
- The participant said that the content of the list in the overview section is not detailed in subsequent sections in the Setup an Fdroid App Repo page.
- It seems more logical for him if in the main page of the documentation are placed first the tutorials and in the end the FAQs.
- The participant had to use the Ctrl + F function several times to find keywords in the index file of the documentation. It seemed unclear and messy to him.
MetaData
All but one of the participants left their app and repository metadata empty during this task. There is a possibility that this is because it was not explicitly stated in the tasks requirements, because it is not clearly marked in the instructions, or because the overall difficulty of the other components of this task distracted them from this component of the task.
Feedback:
- The participant did not complete the repository or application metadata.
- The metadata of the apps and the server was not configured, however the server was running with the given applications.
- The participant did not place the metadata of applications or repository.
- The participant generated the skeleton metadata and did not update the information.
- The participant modifies the metadata files in the visual environment of the local machine (Nautilus and Gedit) because it was more comfortable.
Docs to help address errors
When participants did encounter errors there was little assistance to be found in the existing documentation. The current documentation assumes success. Participants who encountered errors desired that the documentation also included guidance about what could have gone wrong when they encounter errors.
Feedback
- The participant felt frustrated because he did not find a place in the documentation where he could consult errors.In many times, he wanted to use Google to help with the debug process but would not find relevant information there either. The participant wanted a section in the documentation showing how to validate the steps of the process and again a section with common problems in the implementation and configuration.
- Documentation should have a guide of error messages which can be received, e.g. those related to the metadata.
- The participant says that it could be useful a section in the documentation for Troubleshooting
Android Dependencies
Multiple participants were unclear about what android related dependencies were required and how to obtain them.
Feedback:
- The participant seeks for information on how to download Android Studio
- The participant was confused about the need to install the dependencies related to Android in order to complete the task. After reviewing the documentation, the participant decided not to install these dependencies.
- Documentation should be more evident regarding to dependency management. e.g. If the binary installation includes Android dependencies.
- The participant doubts whether to do the setup to create app builds, and if the installation of the corresponding dependencies is covered with the installation itself of Fdroid server.
Task 2: Connect to that repository using the F-Droid client.
- Average Time: 13 Minutes
- Number of Participants with Critical Errors: 2
HTTPS Defaults on Repository Address
Even though the developers thought the client was relatively easy to use some encountered issues related to the assumptions that F-Droid makes around the security of a repository.
When adding a new repository to the client application if the participant leaves the protocol blank (e.g. no HTTP or HTTPS) the client defaults to using HTTPS. If the server does not support HTTPS the repository will fail to set up. A repository that does not support HTTPS is clearly undesirable. But, even so, F-Droid’s implicit assumption, without accompanying documentation and/or errors to alert the developer and participant, caused issues for participants.
Feedback:
- The error the participant was experiencing was that the client by default adds the HTTPS protocol to URLs that don’t explicitly state HTTP(s), and the server used for the task did not support HTTPS.
- It should have had documentation on how to input the URL of the repository to be properly recognized.
- The participant received errors when setting the repository address incorrectly with HTTPS as was suggested by default on the client application on the android phone. Then the participant noticed the situation and changed the address to HTTP.
- The client is intuitive to use.
- The solution to the issue presented does not seem complex to the participant but is not documented and is liable to make mistakes.
Interconnected Documentation Needed
When switching from building a repository to using the repository the participants had to search for client documentation in other parts of the F-Droid website and online. Multiple participants suggested that client documentation related to the use of the F-Droid server being set up should be more easily accessed from the server setup documentation.
It should be noted that the participants were using a development build of the new documentation, and, as such it was not directly linked to the F-Droid website where the client documentation is available.
Feedback:
- In the documentation, there was no information about how setup the client’s app.
- The client documentation should be accessible in the server-setup documentation. For example, including how to install and setup the client.
- The participant claimed the task was completed, however the connection was not successful because he wrongly placed the URL repository in the Android client (root@1xx.1xx.1xx.1xx:/var/www/html /). The participant was then assisted to move on to the next activity.He explains that in the client FAQ does not appear how to fill the URL of new repositories in the client
- Very confused about how to get started.
- Within the app was easy to complete the task, since it is an intuitive application. It becomes necessary to have a step-by-step list of how to set the repositories in the client, especially the URLs.
- A link to home of fdroid.org could be placed in the documentation.
Task 3: Group the applications under your repositories name in the F-Droid interface.
- Average Time: 1 Minute
- Number of Participants with Critical Errors: 0
MetaData
Participants had quick success and no critical errors during this task. But, the participants achieved this by circumventing the aim of the test. Instead of appropriately setting the metadata of their app, and searching for it within the Client, they disabled all other repositories to make it so that only their apps showed in the client. This rapid and common adoption of this specific method of circumventing the need to set, and use, metadata is specifically troubling.
Feedback:
- The participant felt confused about what was expected in the task. However, he thought that disabling other repositories on the client list could be enough.
- There should be an option to disable all repositories included in the software.
- At the beginning, it was confusing to understand which switches had to be disabled and which ones to enabled in order to see the applications of the own repository. It was simple a few seconds later but it should be specified in the documentation.
- There should be in the documentation an instructive manual on the use of the client to manage repositories.
- The participant found very easy to disable other repositories in order to see only the applications of the server used
Task 4: Download the barcode scanner application using the F-Droid client.
- Average Time: 15 Minutes
- Number of Participants with Critical Errors: 2
The issues that the participants faced in this task were actually related to earlier tasks with “critical issues” that were undetectable until this point. Without the file permission issues, described below, downloading apps was seen as a very easy task. This highlights the overall feeling by the developer participants that the client is generally easy and intuitive to use.
Server Permissions
The participants encountered multiple difficult to diagnose issues related to file permissions on the remote server. These issues only appear once a participant is attempting to download an application from a F-Droid repository. As such, permission issues can easily slip past a repo maker who merely updates their repository and checks to ensure that it can be connected to.
Feedback:
- The participant received in the Android client the error “Unsuccessful Non-critical error download”, understood at the time as a permissions error on the (min 1) remote server, which he modified directly at the time by accessing through SSH before re-testing the download.
- Extremely comfortable and fast if the operation of permissions on the Subjective remote server is known. The participant works with this permissions evaluation management every day and says that’s why it became so easy, but perhaps for another person without such familiarity on web servers could be more complicated.
- “It’s easy once you know how to configure file permissions.”
- The participant did not locate any documentation about remote server configuration, especially related to file permissions on the web server. The participant suggests that for many people this would be necessary.
- In the documentation, the information about the file permissions and configuration of the server at Fdroid level is missing. The documentation should say what permissions contain the generated files, (or what permissions they should contain).
- The participant understood how to resolve the permissions problem on the remote server and corrected it by placing 775 permissions on the remote server’s files. However other actions meant that the activity could not be completed successfully.
- The client displayed the error “Connection refused”, the participant concluded that it was due to a problem of permissions on the remote server, however decided to address it by modifying the nginx configuration file, resulting in the inability to read and download files from the remote server.
Task 5: Update the F-Droid repository with an update to the barcode scanner app.
- Average Time: 9 Minutes
- Number of Participants with Critical Errors: 0
Updating the Server
Some participants had continued difficulty working with the server during updates. While some of this was related to difficulty differentiating tasks that should be conducted on the client vs. those that should be conducted on the server when reading the documentation, others were related to the behavior of the software.
Feedback:
- The upgrade process is better documented compared to other parts of the documentation, but still could be more detailed.
- The terminal was giving an error on the local machine when running the update command saying “CRITICAL: Failed to get repo pubkey!”, later the participant discovered that the update was pushed anyway to the server saying that the task was completed.
- The participant felt confused about which commands must be executed in the local machine and which commands in the remote evaluation server. The participant says that if he needs to configure an exclusively local instance he would not know how to do it. The participant says that it could be useful a section in the documentation for Troubleshooting
- The participant does not know exactly where to place the update files.
- The participant is not clear whether it is necessary to run the command fdroid update and then fdroid server update, or just by running fdroid server update would both of the commands run automatically.
- The participant cannot read the update from the client and doubts whether to run a command on the remote server as part of the update process, then he solves by doing update of the local repository before pushing the remote server.
- The participant was not clear if Fdroid update, actually updates the remote server, then after running it he was able to access via SSH to the remote server in order to check if the updated application was present, when seeing that it was not updated, the participant understood that he also had to run Fdroid server update
Documentation is Intuitive Once Understood
Once participants got comfortable with the documentation, server setup, and/or updating process they felt that it was relatively easy to use.
Feedback:
- Very well designed software to handle the updates, it ends up being very easy to use.
- The task was easy once you understand the file structure in the repository.
- The task was very pleasant to complete at the software level.
- Documentation is clear but yet confusing at first reading.
- The upgrade process is better documented compared to other parts of the documentation, but still could be more detailed.
Task 6: Download the update using the phone.
- Average Time: 7 Minutes
- Number of Participants with Critical Errors: 1
Permissions Cont.
Permissions issues that went unaddressed in task 5 caused issues during the, otherwise very easy task, of downloading updates to an application.
Feedback:
- Once understood the issue of file permissions on the remote server, is easy to address the download of the update.
- It’s easy once you know how to configure file permissions.
- Replaying of the same issue of permissions and the error “Download unsuccessful”, then resolved by knowing how permissions are handled on the remote server.
- It is missing in the documentation that before doing “fdroid server update” the permissions of the files to be served can be changed locally since they are transmitted to the remote server with the same local permissions.
- Very pleasant on the Android client side, but it should be documented the type of permissions that the files on the remote server should contain.
- The update is loaded in the remote repo but it does not show on the
- Fdroid client, then the participant suspects it is because of the file permissions. After 12 minutes the participant says that he does not know how to fix the issue and stopped the task. The participant suspects before notifying the failure in the task completion that the issue could be related to some commands and files created as root that creating conflicts with the tasks triggered by the server update command.
Miscellaneous Feedback and Requests
Complexity of Language in the Documentation
- One participant used Google Translator for a better understanding of some terms within the documentation. This participant was also the only participant who speaks English as their primary language. All other participants speak Spanish as their primary language.
Documentation requests
- One participant wanted example configuration files in the Gitlab repository of F-Droid-server.
More explicit documentation
- The documentation must specify that a set of files has been created when fdroid init runs
- It should have specified that commands with Fdroid should be executed in the main directory of the repository (e.g. ~/fdroid) and not in other directories within it (e.g. ~/fdroid /repo).